Balance Sheet Reconciliation: Complete Guide for 2026

No matter what role you play in your accounting team, you know there’s no way around account reconciliations and balance sheet reconciliations. Balance sheet reconciliation is the cornerstone of accurate financial reporting, yet many organizations still rely on outdated spreadsheets and manual processes that should be a thing of the past.
Balance sheet reconciliation helps identify errors, improve accuracy, and support better financial management and decision-making. When done correctly, this reconciliation in accounting ensures your financial statements accurately represent business transactions. However, this essential procedure can easily overwhelm financial teams and become rife with mistakes—especially as businesses grow or when key staff are unavailable during critical periods.
The solution lies in automation. Modern tools expedite the process, dramatically improve accuracy, and deliver significant cost savings. Modern accounting software with built-in reconciliation modules can further streamline the process, and training teams to use such software is crucial for maintaining accurate and efficient financial practices. In this guide, we’ll explore how to do reconciliation effectively, demonstrate how automation revolutionizes the process, and show how your accounting team can shift from manual tasks to high-value analytical work.
Coming Up
What is Balance Sheet Reconciliation?
Why Balance Sheet Reconciliation Matters
Step-by-Step Reconciliation Process
Automation Tools for Reconciliation
Best Practices for Financial Accuracy
Balance Sheet Reconciliation Checklist
Real-World Example of Reconciliation
Final Thoughts: Modernizing Your Process
What is Balance Sheet Reconciliation?
Balance sheet reconciliation is the process of verifying that account balances in your company’s general ledger and each general ledger account accurately match corresponding balances in supporting documents. This reconciliation in accounting ensures your financial statements reflect true business performance and maintains the integrity of your financial reporting.
In every business, balance sheet reconciliation takes place at defined intervals—monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Balance sheets list assets and liabilities, and every transaction must be categorized correctly. During reconciliation or the closing of accounts, businesses verify that everything has been documented accurately. It is important to reconcile balance sheet accounts to ensure the accuracy of assets, liabilities, and equity, supporting transparency and efficient financial closing. This is done by comparing general ledger balances with external sources like bank statements, vendor invoices, and payment records.
As you know, your balance sheet is one of the essential documents in your business. It can help prove creditworthiness for a bank loan or demonstrate to investors how your company is performing financially, while balance sheet reconciliation supports the integrity of the company's financial statements and overall financial health.
Key Accounts in Balance Sheet Reconciliation
Typically, balance sheet reconciliations involve reconciling these critical accounts:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Accounts Receivable
- Accounts Payable
- Prepaid Expenses
- Inventory
- Payroll Liabilities
- Accrued Liabilities
- Loans and Debt
- Fixed Assets
- Deferred Revenue
- Other Balance Sheet Accounts
General Ledger Reconciliation
General ledger reconciliation is a foundational element of the balance sheet reconciliation process, serving as a critical checkpoint for financial accuracy. This process involves systematically verifying that the account balances recorded in your general ledger align with the figures found in supporting documentation, such as bank statements, invoices, and payment records. By comparing these sources, you can quickly identify discrepancies or errors that may impact your financial reporting and the reliability of your financial statements.
A robust general ledger reconciliation process relies on solid internal controls, including clear segregation of duties and regular, independent reviews. These controls help prevent fraud and minimize the risk of human error, ensuring that every transaction is properly recorded and classified. Best practices, such as leveraging automation and conducting regular risk assessments, can further streamline the reconciliation process, reducing manual tasks and increasing efficiency.
Ultimately, effective general ledger reconciliation not only supports the integrity of your balance sheet but also strengthens your company’s overall financial reporting. By maintaining accurate account balances and thorough supporting documentation, you lay the groundwork for reliable financial statements and confident business decision-making.
Why Balance Sheet Reconciliation Matters
Balance sheet reconciliations play a pivotal role in ensuring accurate financial reporting and enhancing operational efficiency, while also ensuring the company's financial position is accurately reflected. Balance sheet reconciliation is important because it helps prevent errors, reduces the risk of fraud, and supports compliance with regulatory requirements, all of which are critical for financial accuracy and reliability. Understanding how to do reconciliation properly contributes directly to business success across multiple dimensions.
Maintaining balance sheet integrity is essential for building trust in financial statements and supporting sound business operations.
Accuracy and Trust
Balance sheet reconciliations are crucial for preventing errors, fraud, and financial misstatements that can damage your business reputation. As a core accounting practice, they ensure the accuracy of financial statements by ensuring financial accuracy through the verification and comparison of financial records, providing essential insights into the financial health of your business.
Prevents Critical Financial Issues:
- Spots Errors: This process helps identify omissions, errors, or misclassifications that could otherwise adversely affect financial statements. Reviewing the company's financial records during reconciliation is essential for detecting issues early and maintaining reliable financial data.
- Resolves Issues: Provides a mechanism to correct discovered errors, ensuring the integrity of financial reporting
- Builds Stakeholder Confidence: Accurate reconciliations enhance credibility with investors, lenders, and business partners
Consider the real-world implications of infrequent reconciliations: after depositing a check, your bank balance increases, but this might not reflect actual cash available if funds have been allocated to pay vendors. Regular balance sheet reconciliations allow businesses to accurately determine their cash positions and support the integrity of the company's financial records, helping to ensure overall financial accuracy and compliance.
Compliance Benefits
All businesses must complete the financial close process monthly to guarantee their financial statements accurately reflect their current state. Account reconciliation is a key component in meeting regulatory requirements and maintaining regulatory compliance, including ensuring regulatory compliance with standards like GAAP and IFRS. This process is essential for:
- SOX Compliance (Sarbanes-Oxley Act requirements)
- GAAP Standards (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
- IFRS Guidelines (International Financial Reporting Standards)
- Internal Controls Documentation: Well-executed reconciliations create reliable audit trails and thorough process documentation
These comprehensive records enhance the credibility of financial reports during external audits and regulatory reviews, ensuring your organization meets all compliance obligations. Thorough reconciliation also supports accurate and timely disclosures, which are essential for audits and regulatory reviews.
Financial Decision-Making
Through effective general ledger reconciliation, businesses gain detailed insights into their financial activities, identifying areas of spending and earnings. This information is crucial for:
- Real-time Decision Making: Accurate cash positions facilitate informed financial decisions through data automation
- Operational Efficiency: Enhanced visibility into financial activities helps reduce costs and improve processes
- Transaction Transparency: Complete reconciliation provides detailed insights into all financial transactions
Account reconciliation is essential for accurately matching and verifying records, enabling businesses to close their books on time and make strategic decisions based on reliable financial data. Accurate reconciliation also ensures the integrity of the company's financial statements, providing confidence to stakeholders and decision-makers.
Step-by-Step Reconciliation Process
Learning how to do reconciliation effectively requires following a systematic approach. Documenting the entire reconciliation process is crucial for ensuring accuracy and audit readiness. This general ledger reconciliation process ensures accuracy while maintaining efficiency throughout your monthly close cycle.
Step 1: Identify Key Balance Sheet Accounts to Reconcile
Start by determining which accounts require reconciliation based on:
- Risk level and materiality (high-value or high-risk accounts first)
- Regulatory requirements (cash, debt, equity accounts)
- Ensure coverage of all major categories, including assets, liabilities, and equity, to maintain accurate financial statements
- Business-critical accounts (accounts receivable, accounts payable)
- Accounts with frequent activity or complex transactions
Pro Tip: Create a reconciliation checklist prioritizing accounts by importance and compliance requirements.
Step 2: Gather Documentation (GL, Bank Statements, Invoices)
Collect all necessary supporting documents for each account:
- General Ledger reports for the specific period
- Bank statements and transaction records
- Credit card statements and reconciliations
- Vendor invoices and payment confirmations
- Customer statements and receipts
- Loan agreements and amortization schedules
- Investment statements and market valuations
Ensure all documents cover the same reporting period and are complete before beginning the comparison process.
Step 3: Compare GL Balance to Supporting Documentation
Systematically compare your general ledger balance with supporting documentation:
- Compare transactions and match individual transactions between the GL and external records to ensure accuracy
- Identify the ending balance from each source
- Note any immediate discrepancies in amounts, dates, or transaction details
- Flag unusual items that require further investigation
Use reconciliation templates or software to standardize this comparison process across all accounts.
Step 4: Investigate Discrepancies (Errors, Timing Issues)
When differences arise, investigate systematically:
- Timing differences: Outstanding checks, deposits in transit, or end-of-period cutoff issues
- Recording errors: Transposed numbers, incorrect amounts, or duplicate entries
- Missing transactions: Unrecorded bank fees, interest, or other activity
- Classification errors: Transactions posted to wrong accounts
Documentation is key: Record your findings and the source of each discrepancy for audit trail purposes.
Note: While expense accounts and other income statement accounts are important for financial reporting, they are typically not the focus of balance sheet reconciliation. This is because expense accounts appear on the income statement and are reset each period, whereas balance sheet accounts carry their balances forward and require ongoing reconciliation.
Step 5: Adjust Journal Entries as Needed
Based on your investigation, make necessary corrections as a critical part of balance sheet account reconciliation:
- Create adjusting journal entries for legitimate discrepancies
- Correct coding errors by reclassifying transactions
- Record missing transactions identified during reconciliation
- Reverse duplicate entries or other posting errors
Important: All adjustments should be properly authorized and documented with supporting evidence.
Step 6: Finalize and Document the Reconciliation
Complete the reconciliation process by:
- Verifying final balances match between GL and supporting documentation
- Preparing reconciliation summaries showing all adjustments made
- Obtaining required approvals from supervisors or controllers
- Completing balance sheet certification using automated or routine processes to ensure accuracy and efficiency in verifying account balances
- Filing supporting documentation for audit and compliance purposes
- Updating reconciliation logs with completion status and any outstanding items
This documentation serves as your audit trail and supports the integrity of your financial reporting process.
Common Challenges & Pitfalls
The Excel spreadsheet was once a beacon of hope for accounting teams everywhere. While it’s still a powerful tool, it can easily become a horrible master. If you’re stuck relying on spreadsheets for balance sheet reconciliation, you’re going to run into a slew of hurdles. Manual processes that should be a thing of the past are compounded by disparate and disconnected data across multiple systems, which increases errors and inefficiencies.
Manual Reconciliation via Spreadsheets
Manual transaction matching takes enormous amounts of time and introduces significant risk. As talented as your team is, manual errors are inevitable when working with data by hand, becoming increasingly risky when generating financial statements. Tracking and managing reconciliation tasks manually further increases the risk of oversight and delays, as it becomes difficult to monitor responsibilities and progress in real-time.
Common examples:
- Human error in Excel formulas: Misplaced cell references throwing off entire reconciliations
- Duplicate journal entries: Accidentally recording the same transaction multiple times
- Data entry mistakes: Transposing numbers or copying incorrect amounts
Disconnected Systems and Siloed Data
With more teams working remotely, siloed data causes even greater risks. If data is stored across desktops in spreadsheets, it’s not connected, which means it may be outdated or duplicated. Your team needs to manually collect data from different sources, which is a huge time drain. Well-defined accounting processes can help mitigate the risks of disconnected systems by ensuring structured procedures for data management and supporting accurate financial records.
Time-Intensive Review Cycles
Traditional reconciliation processes consume excessive time through extended data gathering, lengthy investigations, and repetitive verification tasks. Approval delays during financial close occur when reviewers are unavailable or overwhelmed, further extending close cycles.
Lack of Internal Controls
Without proper oversight, reconciliation efforts become inconsistent and create compliance risks:
- No reviewer assignments: Reconciliations completed without independent verification
- Missing version history: No audit trail of changes or corrections made
- Insufficient approval workflows: Important adjustments proceeding without authorization
These limitations highlight why many organizations are transitioning to automated reconciliation solutions.
Automation Tools for Reconciliation
Modern accounting technology has revolutionized how to do reconciliation, transforming traditionally manual processes into streamlined, accurate workflows. Automation solutions, such as Solvexia, address the fundamental challenges of manual reconciliation while enhancing overall financial close efficiency.
Key Automation Benefits
- Centralized Data Management: Automation platforms consolidate financial data from multiple sources into a single system, eliminating the disconnected spreadsheets and siloed information that plague manual processes. This centralization ensures all team members work with consistent, up-to-date information.
- Real-Time Transaction Matching: Advanced matching algorithms automatically identify and reconcile transactions across different systems, reducing hours of manual work to minutes. Real-time processing means discrepancies are caught immediately rather than discovered weeks later.
- Workflow Standardization: Automated solutions enforce consistent reconciliation procedures across all accounts and team members, ensuring every balance sheet account is reconciled consistently. Standard templates and workflows ensure nothing falls through the cracks while maintaining audit compliance.
- Significantly Reduced Errors: By eliminating manual data entry and calculation errors, automation dramatically improves accuracy. Built-in validation rules catch potential issues before they impact financial statements.
Leading Solutions: Solvexia Features
Solvexia exemplifies modern reconciliation automation with enterprise-grade capabilities designed for growing businesses:
- Drag-and-drop workflow builder: Create custom reconciliation processes without IT involvement, adapting to your specific business needs
- Comprehensive audit trail: Automatically track every change, approval, and adjustment with complete documentation for compliance requirements
- Real-time dashboards: Monitor reconciliation progress across all accounts with instant visibility into completion status and outstanding items
These automation tools enable finance teams to complete general ledger reconciliation 100x faster with 98% fewer errors, freeing up valuable time for strategic analysis and decision-making.
Best Practices for Financial Accuracy
Effective balance sheet reconciliation requires systematic approaches that ensure accuracy while maintaining efficiency. Implementing robust internal controls, such as segregation of duties and regular reviews, is essential in the reconciliation process to prevent fraud and ensure compliance.
These proven practices help organizations master how to do reconciliation consistently. A well-structured closing process further supports timely and accurate reconciliations by streamlining steps and reducing errors.
Schedule Reconciliations Regularly
- Monthly reconciliations for high-activity accounts (cash, A/R, A/P)
- Post-close reconciliations to validate final financial statement balances
- Real-time monitoring for critical accounts with daily transaction volumes
Use Standard Templates Across Teams
Implement consistent reconciliation formats with standardized workpapers, uniform documentation requirements, and template libraries for different account types. This ensures quality consistency regardless of who performs the reconciliation.
Separate Roles for Preparer/Reviewer
Establish clear segregation of duties with dedicated preparers, independent reviewers, and supervisory approval for significant adjustments. This separation provides essential checks and balances while maintaining audit compliance.
Review Aging Reports and Accruals
Regularly analyze account details beyond balance matching:
- Aging analysis for receivables and payables
- Accrual reviews to ensure completeness of recorded liabilities
- Cutoff testing to verify proper period recording
Maintain Supporting Documentation and Audit Trail
Ensure comprehensive documentation including source documents, detailed workpapers, clear explanations for reconciling items, and proper approvals for audit compliance.
💡 Pro Tip: Set materiality thresholds for review to prioritize high-impact accounts. For example, require supervisor approval for reconciling items over $10,000, while allowing automatic acceptance of differences under $500.
Balance Sheet Reconciliation Checklist
Whether using automation or working through balance sheet reconciliation manually, follow this essential checklist to ensure you're hitting every mark in your reconciliation in accounting process:
☑️ Pull Internal + External Documents
Gather all necessary documentation for your general ledger reconciliation:
- Bank statements and transaction records
- General ledger or account balance exports
- Receipts, invoices, and vendor statements
- Investment statements and loan documentation
Automation solutions can pull together all this data instantly, while manual processes require systematic collection from multiple sources.
☑️ Perform Transaction Matching
The heart of reconciliation is transaction matching. With all documentation assembled, systematically cross-check entries between your general ledger and supporting documents. This step can take significant time with manual processes but happens instantly with automated solutions.
☑️ Adjust Discrepancies
When discrepancies are identified, create appropriate journal entries to rectify them. Document the reason for each adjustment and maintain proper version control throughout the correction process.
☑️ Review with Second Set of Eyes
Have an independent reviewer verify the reconciliation work:
- Confirm all adjustments are properly supported
- Validate transaction matching accuracy
- Approve significant reconciling items before finalizing
☑️ Store Final Documentation
Maintain comprehensive records including completed reconciliations, supporting documents, and approval signatures. This documentation serves as your audit trail and supports compliance requirements.
Final Step: Ensure that balance sheet totals equate your assets to liabilities and equity—confirming the fundamental accounting equation balances perfectly.
Real-World Example of Reconciliation
Let's walk through a practical example of how to do reconciliation using a cash account. This general ledger reconciliation demonstrates the typical process and resolution steps.
Cash Account Reconciliation Walkthrough
Starting Balances:
- General Ledger Cash Balance: $100,000
- Bank Statement Balance: $98,000
- Variance to Investigate: $2,000
Investigation Results: The $2,000 difference consists of outstanding checks—checks written but not yet cleared the bank.
Resolution: This is a timing difference, not an error. Outstanding checks are normal reconciling items, so no journal entry adjustment is needed. Simply document the reconciling item with supporting check details for your audit trail.
Final Result: Both balances effectively represent $98,000 in available cash once outstanding checks are considered.
When Adjustments Are Required
For comparison, consider an accounts receivable scenario where investigation reveals a $10,000 client discount was processed in the subledger but not the general ledger. This requires a journal entry adjustment to bring balances into alignment.
The key is determining whether variances represent timing differences (no adjustment needed) or actual errors requiring correction.
Final Thoughts: Modernizing Your Process
Balance sheet reconciliations should provide significant benefits when you balance accuracy with efficiency. Since balance sheets are like a report card for your business, they should accurately reflect performance while not overwhelming your team with manual processes.
Modern reconciliation in accounting has evolved beyond spreadsheets and manual tracking. With automation tools like Solvexia, your team achieves enhanced accuracy, reduced processing time from hours to minutes, and eliminated human errors.
The world of disconnected spreadsheets is becoming obsolete. Welcome to a new frontier where software systems help your business function better, faster, and stronger.
Ready to transform your process? Request a demo to see how Solvexia streamlines reconciliation.
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

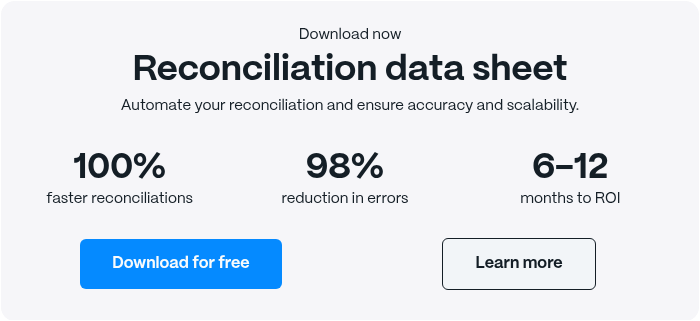
Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)