What is Data Reconciliation? Best Practices, Tools, and Importance

When you have access to seemingly infinite data, it only makes sense to put it to good use for business insights and decision making capabilities. To do so properly, data reconciliation must take place, as it is essential for ensuring accurate data and data consistency across systems—both of which underpin effective decision-making and operational efficiency. But, how can you manage all the data in so little time?
We’re going to share some data reconciliation best practices and take a look at the best reconciliation software to streamline the heavy lifting.
What is Data Reconciliation?
Data reconciliation is the process of ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and integrity by systematically performing the process of comparing data from various sources during migration and integration phases. When transferring data between systems, this crucial verification step ensures that target data matches source data perfectly. Data reconciliation tools use sophisticated mathematical models and data matching algorithms to compare datasets, identify data inconsistencies, and support error detection, allowing organizations to identify and resolve discrepancies before the information is used for business intelligence.
For example, a retail company might use data reconciliation techniques to verify that sales data from their point-of-sale systems matches their inventory management system. This type of data reconciliation example shows how businesses can maintain data integrity across multiple platforms. Additionally, data reconciliation helps detect anomalies and fraud, acting as a defense in cybersecurity.
Why is Data Reconciliation Important?
Data reconciliation serves as checks and balances so that you can trust your data with high confidence and remove the risk of errors.
Enables Confident Decision-Making
When making decisions within an organization, you want to remove the guesswork as much as possible. Naturally, the go-to place for verification before moving forward relies on the data - numbers and figures don't lie! That is, if they are correct in the first place. Improved data accuracy enhances decision-making, boosts trust in reporting and analysis, prevents errors, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Ensures Data Integrity Across Systems
Achieving accurate and consistent data through data reconciliation is crucial, especially when dealing with multiple data sources that can lead to discrepancies. Data reconciliation creates a single version of the truth that can be trusted for analytics, reporting, and decision-making. Maintaining data quality and ensuring data integrity are ongoing goals of data reconciliation.
Powers Critical Business Functions
Data can be used to implement new marketing campaigns (based on customer buying preferences), product development (based on product/market fit), and forecasting next steps (based on historical and past events). Data reconciliation efforts support accurate forecasting, reliable performance tracking, and reporting. These are just a few reasons how data can impact a business' overall functions and operations.
Meets Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Regulatory compliance in industries like finance and healthcare requires maintaining data integrity through data reconciliation. Accurate data reconciliation is essential for ensuring data integrity, supporting better decision-making, and meeting regulatory compliance requirements.
Addresses Modern Data Management Challenges
While the influx of data is hardly a challenge, data management and storage has increasingly caused hardship for businesses seeking to modernize their systems. As a result, finance automation solutions have emerged to quell the burden. A tool like Solvexia connects your data systems across the board, centralizes your data, and performs data reconciliation automatically to make sure that your data is always up-to-date, clean, and ready to apply for insights to derive value.
Data Reconciliation in Business Use Cases
Data reconciliation applies across various business functions, each with unique requirements and challenges.
ETL and Data Migration
During ETL processes and system migrations, reconciliation validates that data transfers accurately from legacy systems to modern platforms. Tracking data lineage during ETL and migration is crucial for ensuring data quality, traceability, and resolving discrepancies that may arise during data reconciliation. Pre-reconciliation validation often includes automated 'pre-flight' checks on record counts and field formats to catch issues before the main reconciliation process.
Common checks include row count matching, aggregate verification, and data type consistency. For example, when migrating to a cloud-based ERP, reconciliation ensures all historical transactions and customer records transfer completely, preventing operational disruptions and audit failures. During data migrations, reconciliation also acts as a final validation step to ensure no data loss occurred.
Financial and Regulatory Reporting
Financial reconciliation ensures compliance with regulations like SOX, IFRS, and GAAP. Reconciling financial transactions is crucial for verifying the accuracy of financial records, and organizations use both transaction-level reconciliation and balance-level reconciliation to detect discrepancies and maintain compliance across various platforms and systems.
Organizations match bank statements with internal accounts, subsidiary ledgers with general ledgers, and intercompany transactions across business units. Automated tools maintain audit trails, flag discrepancies immediately, and reduce month-end close times from weeks to days. Best practices for financial reconciliation in 2026 include continuous monitoring and advanced automation.
Customer Data and CRM Systems
Customer data exists across CRM systems, marketing platforms, e-commerce sites, and support databases. Reconciliation maintains consistent information across these touchpoints, preventing duplicate records and mismatched transaction histories. This creates a unified customer view that enables accurate marketing, better sales intelligence, and improved customer experiences.
Accurately matching records across different datasets is especially challenging when unique identifiers are absent or inconsistent.
Data Formats and Reconciliation
Data formats are a foundational element in the data reconciliation process, directly impacting the ability to achieve accurate and consistent data across systems. When organizations gather data from different sources—such as databases, spreadsheets, cloud applications, or legacy systems—each source may use its own data formats for dates, currencies, numbers, or text fields. These inconsistencies can introduce data discrepancies that complicate the reconciliation process and undermine data quality.
Inconsistent data formats often lead to mismatched records, missing values, or errors during data matching. For example, a date field formatted as “MM/DD/YYYY” in one system and “DD-MM-YYYY” in another can cause the reconciliation process to flag false discrepancies, even when the underlying data is correct. Similarly, differences in how currencies or numerical values are represented can result in inaccurate comparisons and reporting.
To ensure data quality and maintain accurate and consistent data, organizations should standardize data formats before beginning the reconciliation process. This may involve implementing data transformation and mapping rules, using automated reconciliation tools that can handle multiple data formats, and establishing clear data governance policies. By proactively addressing data format issues, businesses can reduce data discrepancies, streamline the reconciliation process, and ensure that data from different sources is integrated seamlessly.
Ultimately, managing data formats effectively is essential for maintaining data integrity, supporting accurate reporting, and meeting regulatory compliance requirements. Consistent data formats enable organizations to reconcile data efficiently, minimize errors, and make confident, data-driven decisions.
The Data Reconciliation Process Explained
A systematic data reconciliation process follows four key stages to ensure accuracy and consistency.
1. Data Extraction
The process begins by extracting data from source and target systems. This involves pulling relevant datasets—such as transaction records, customer information, or financial data—from databases, applications, or files. Modern reconciliation tools automate this extraction using connectors and APIs, scheduling regular pulls to ensure data is current and complete.
2. Data Matching and Comparison
Once extracted, the system matches records between source and target datasets using defined keys like transaction IDs, account numbers, or customer identifiers. Automated matching rules handle variations in formats and apply tolerance thresholds for acceptable discrepancies. Automating validation in this stage can improve operational efficiency by reducing manual effort and saving time, allowing teams to focus on resolving exceptions and addressing data quality issues.
3. Discrepancy Resolution
When the comparison reveals differences, the system flags these discrepancies for investigation. The goal is to ensure data accuracy through resolution and correction of discrepancies. Teams analyze each variance to determine its root cause—whether it’s a timing difference, data entry error, system glitch, or transformation issue. Depending on the findings, discrepancies are corrected at the source, adjusted in the target system, or documented as acceptable differences with proper justification. Resolution and correction of discrepancies can be done automatically based on predefined rules or manually by data stewards, involving updating records or merging duplicates.
4. Final Validation and Documentation
After resolving discrepancies, a final validation confirms all data matches within acceptable parameters. The system generates comprehensive documentation including reconciliation reports, audit trails showing all changes made, exception logs detailing unresolved items, and sign-off records for compliance purposes. This documentation provides transparency for audits and creates a reference for future reconciliation cycles.
Manual vs Automated Data Reconciliation
Organizations can choose between manual and automated approaches, each with distinct advantages and limitations.
Pros and Cons
Manual Data Reconciliation
Pros:
- Lower upfront costs with no software investment required
- Greater flexibility for one-off or unique reconciliation scenarios
- Direct human oversight and judgment on complex discrepancies
- No technical implementation or training period needed
Cons:
- Extremely time-consuming, especially with large data volumes
- High error rates due to human mistakes in data entry and comparison
- Difficult to scale as business grows and data increases
- Lacks audit trails and compliance documentation
- Limited real-time capabilities for urgent reconciliation needs
Automated Data Reconciliation
Pros:
- Processes large datasets quickly—up to 100x faster than manual methods
- Significantly reduces errors through consistent rule application
- Provides real-time reconciliation and immediate discrepancy alerts
- Generates automatic audit trails for compliance and reporting
- Scales easily as data volume grows without adding headcount
Cons:
- Requires upfront investment in software and implementation
- Initial setup time needed to configure rules and connections
- May need technical expertise for complex customizations
- Ongoing maintenance and updates to reconciliation rules
For most organizations handling significant data volumes or facing regulatory requirements, the benefits of automation far outweigh the initial investment costs.
Data Reconciliation Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Organizations frequently encounter several key challenges when implementing data reconciliation processes. Understanding these challenges and having strategies to address them is crucial for successful data management.
1. Siloed Systems and Data Sources
Challenge: Many organizations operate with multiple systems that don’t naturally communicate with each other, creating data silos that complicate reconciliation efforts.
Solution:
- Implement integration platforms that connect different systems
- Use data reconciliation tools with built-in connectors
- Adopt standardized data formats across systems
2. Manual Processing Bottlenecks
Challenge: Traditional manual reconciliation processes are time-consuming, error-prone, and can't scale with growing data volumes.
Solution:
- Leverage automation tools for routine reconciliation tasks
- Use no-code platforms that empower business users
- Implement automated exception handling
3. Complex Data Transformations
Challenge: Data from different sources often comes in varying formats and structures, making comparisons difficult.
Solution:
- Use modern data reconciliation tools with built-in transformation capabilities
- Implement standardized data mapping processes
- Utilize no-code transformation tools for business users
4. Real-time Reconciliation Needs
Challenge: Modern businesses need near real-time data validation, which is impossible with manual processes.
Solution:
- Deploy automated reconciliation systems with real-time capabilities
- Set up automated alerts for discrepancies
- Use streaming data processing for continuous reconciliation
5. Compliance and Audit Requirements
Challenge: Meeting regulatory requirements while maintaining efficient reconciliation processes can be complex.
Solution:
- Implement automated audit trail generation
- Use tools with built-in compliance reporting
- Maintain detailed documentation of reconciliation rules
Effective data governance is crucial in establishing a framework that includes policies and guidelines for data reconciliation, ensuring accuracy and integrity in data management.
By addressing these challenges with modern data reconciliation tools and automation solutions, organizations can significantly improve their data quality and operational efficiency.
Best Practices for Data Reconciliation
To ensure successful data reconciliation implementation and maintenance, follow these comprehensive best practices:
1. Establish Data Quality Standards
- Define acceptable tolerance levels for different types of data
- Create clear data validation rules and criteria
- Document expected formats and standards for all data sources
- Set up data quality scorecards for regular monitoring
2. Implement Strong Controls
- Establish segregation of duties for data validation and approval
- Create detailed audit trails for all reconciliation activities
- Set up multi-level review processes for critical data sets
- Define clear escalation paths for discrepancies
3. Automate Strategically
- Start with high-volume, routine reconciliations
- Build automated validation rules based on historical patterns
- Configure real-time alerts for significant variances
- Implement automated documentation of reconciliation results
4. Address Discrepancies Promptly
- Establish SLAs for investigating and resolving differences
- Create a standardized process for documenting resolution steps
- Maintain a knowledge base of common issues and solutions
- Regular review of unresolved items to prevent backlog
5. Maintain Data Hygiene
- Regular cleansing of master data
- Periodic review and updates of matching rules
- Scheduled maintenance of reference data
- Routine cleanup of historical reconciliation records
6. Monitor and Improve
- Track reconciliation completion rates and timing
- Measure error rates and resolution times
- Analyze patterns in discrepancies to prevent future issues
- Regular review and updates of reconciliation rules
7. Focus on Training and Documentation
- Develop comprehensive procedure manuals
- Provide regular training for team members
- Document system configurations and changes
- Maintain updated user guides for reconciliation tools
Top Data Reconciliation Tools in 2026
When selecting a data reconciliation tool, prioritize solutions that offer automation capabilities, seamless integration with existing systems, real-time processing, comprehensive audit trails, and user-friendly interfaces.
1. Solvexia
A comprehensive finance automation platform designed for complex reconciliation and financial processes. Features no-code automation with drag-and-drop functionality, extensive data connectors for legacy and modern systems, and real-time reconciliation capabilities. Organizations typically reduce errors by 98% and run processes 100x faster. Ideal for teams handling reconciliation, financial reporting, expense management, and rebate management without dedicated IT support.
2. BlackLine
A leading cloud-based solution focused on financial close and account reconciliation. Offers task management, automated matching, and continuous accounting capabilities. Particularly strong for large enterprises with complex month-end close processes and SOX compliance requirements.
3. Trintech
Provides end-to-end financial close and reconciliation management with strong controls and compliance features. Excels in transaction matching, variance analysis, and certification workflows. Well-suited for mid-to-large enterprises in regulated industries.
4. ReconArt
Specialized reconciliation software with flexible matching logic and extensive data source connectivity. Offers customizable workflows and automated exception management. Popular among financial institutions and organizations with high-volume transaction reconciliation needs.
5. Oracle Account Reconciliation
Part of Oracle's EPM Cloud suite, offering enterprise-grade reconciliation with robust security and compliance features. Integrates seamlessly with other Oracle systems and provides detailed audit trails. Best for organizations already invested in the Oracle ecosystem.
Data Reconciliation vs Data Validation
While often used interchangeably, data reconciliation and data validation serve distinct purposes in ensuring data quality.
Data Validation checks whether individual data entries meet predefined rules, formats, and constraints. It verifies data is correct, complete, and conforms to expected standards—such as ensuring an email contains an "@" symbol or a required field isn't blank.
Data Reconciliation compares data across different systems or datasets to ensure consistency. It verifies that the same information matches across multiple sources—such as confirming sales figures in your CRM match revenue in your accounting system.
Key Differences:
- Scope: Validation checks individual data quality; reconciliation compares across systems
- Timing: Validation occurs at data entry; reconciliation happens during transfers or periodically
- Purpose: Validation ensures correctness; reconciliation ensures consistency
Both processes are essential—validation prevents bad data from entering systems, while reconciliation ensures data remains accurate as it moves between systems.
Final Thoughts
Having data available in your business is just the beginning of being able to derive value from the figures. In order to transform the data into insights, data reconciliation must take place to validate your data.
As data volume grows and your workload increases, the need for reconciliation reporting and data reconciliation software also grows. Get started with automation today by requesting a demo from Solvexia - we’re here to help!
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

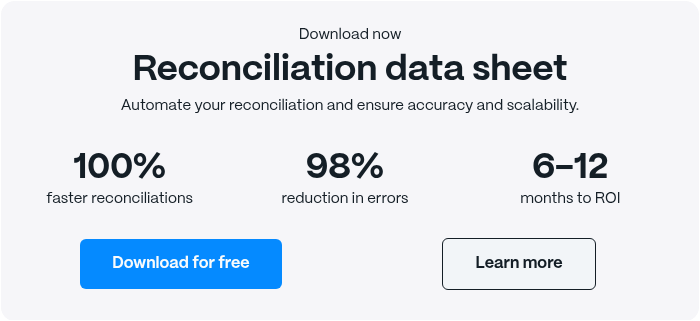
Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)







.jpeg)