Strategic Risk Management: 5 Tips for Success

Successful businesses have to both do the right things and do things right to stay ahead. In terms of action, this means having operations in line and also defining a strategy that works. However, many companies lose out on market opportunities because they ignore strategic risks. While operational risks also post a threat, strategic risks tend to be overlooked more often, yet they can cause more significant impact. This is why strategic risk management is so important.
Here, we will define strategic risk, understand strategic risk management and share five tips for success for its implementation.
Coming Up
2. What are Strategic Risk Examples
3. How to Overcome Different Types of Strategic Risk?
4. Strategic Risk vs Operational Risk
5. What is Strategic Risk Management?
6. Strategic Risk Assessment Process
7. Integrating Strategic Risk Management
8. 5 Tips for Success: Measuring and Managing Risk
11. A CFO’s Approach to Strategic Risk Management
What is Strategic Risk?
In its most simplistic of definitions, strategic risk is the risk associated with failed business decisions. It refers to decisions or events that can get in the way of an organisation reaching its goals.
Strategic risk represents one type of risk that businesses face, along with risks like operational, financial, and regulatory, to name a few. In many instances, strategic risks and the other kinds of risk will impact one another as they are interconnected.
Strategic risk can take place due to competition, market events, changing regulations, compliance, and more. We’ll soon touch on what this could look like in your business.
These types of risks affect overall business strategy, but sometimes they are necessary to reap the rewards. For example, a bank takes on strategic risk by offering credit, but it’s an inherent risk that is directly related to its business goals. Since strategic risk is all centered around “doing the right things,” it may be harder to identify than operational risks, which come down to “doing things right.”
Strategic risks occur when businesses fail to meet the market’s needs. To achieve business goals, companies face dangers and downfalls. Every internal choice comes with the potential of making the wrong choice. To complicate things further, strategic risk isn’t only based on subjective decisions. It can also be caused by externally because of market demand and the environment in which products get released.
What are Strategic Risk Examples
By breaking down strategic risk examples, we can better understand how to overcome them. Here’s a look at what they can be categorised as:
- Competitive risk: This refers to the risk that your competition will gain more market share than you and you will fall behind them in innovation.
- Regulatory risk: The degree to which you must adhere to regulations varies by industry. In highly regulated industries like finance or transportation, this type of strategic risk will clearly be more of a concern. This is because new regulations can affect your business processes, call upon the need for new roles to be created, demand new technologies, and shift your business leaders’ time and focus to having to deal with the regulations.
- Political risk: Changes in the political landscape can affect business’ operations, trade agreements, and more. Additionally, the politics affect security and the supply chain, so politics can pose a risk to businesses.
- Governance risk: Any risk associated with lack of governance or compliance. Again, the degree to which this risk affects your business will depend on your business line. When it comes to data and finances, governance risk is higher (which calls upon the need for more internal controls).
- Economic risk: The overall macroeconomic conditions affect how your business takes place and the success of your business strategy.
- Operational risk: This refers to the day-to-day ways that you execute in business and the risk that processes are not up-to-date. With outdated processes, you may be costing the business more or less productive than you’d otherwise be with process improvement.
- Change risk: Implementing changes within your organisation can create risk in itself if there’s resistance or struggles to adopt the change. Keep in mind that you can practice change management to overcome such risk.
How to Overcome Different Types of Strategic Risk?
The connection between the types of strategic risk can serve to your advantage. It requires a holistic and high-level view of your business, goals, and strategy to decide how to mitigate the strategic risks you may face.
With that said, here are suggestions for overcoming such risks:
- Understand your competition and conduct market research
- Utilise data to your advantage for business intelligence and forecasting
- Remain aware of regulatory changes and adopt technologies and processes that are agile
- Select suppliers and vendors in politically stable countries
- Continuously monitor your business and its practices to protect against financial risks
- Leverage change management such that change is welcomed and understood by everyone involved
No matter what type of strategic risks your business faces, financial automation software can serve multiple purposes. You can rely on having data in a centralised and secure location. You will be able to measure the success of your processes and optimise efficiency. You can conduct data analysis to make use of historical data to predict future events and be prepared.
Strategic Risk vs Operational Risk
To better understand strategic risk, it helps to define what operational risk is to see the differences.
Operational Risk: Operational risks comes from how a business does something, or in other words, their operations. Risks can arise from a breakdown in processes, people or systems. These risks stem from how a business performs day-to-day activities.
Now that we better understand what strategic risk is and isn’t, how do business leaders plan around strategic risk? They implement strategic risk management.
What is Strategic Risk Management?
Once you recognise and acknowledge that strategic risk is inherent in the business, it pays to manage it.
Strategic risk management is the process of identifying risks, analysing their potential effects and taking necessary action to mitigate them. These internal and external risks pose a threat to the business’ strategy and objectives. For example, if a finance company is going to sign a big new client, there is an inherent risk that the company won’t be able to scale quickly to provide the full service with the client needs and what if the client leaves after a short time. However, the finance company is aware of this risk and can plan by hiring part-time staff or keep existing staff and free up their time by driving more efficiencies such as through automation tools to mitigate such risk.
As a focal point under enterprise risk management (ERM), strategic risk management focuses on the types of risks that will affect stakeholder value. As such, executive-level leadership must allocate their time to help manage and face this risk.
Some examples of strategic risk include:
- Technological changes
- Senior management turnover
- Merger integration
- Stakeholder pressure
- Competitive pressure
- Consumer demand shifts
- Consumer preferences changes
- Regulatory changes
It’s critical to assess the impact of strategic risks to prioritise the strategy to manage them. The main two crucial metrics by which to evaluate strategic risks are:
- Economic Capital: This is the amount of equity needed to cover unexpected losses. It’s derived from the company’s target debt rating.
- Risk-Adjusted Return On Capital (RAROC): RAROC helps to understand the return on investment with the risk involved. It determines the return level relative to the risk taken. The calculation is: revenue - expenses - expected loss + income from capital / capital
Strategic Risk Assessment Process
Putting strategic risk management in action involves several steps. It begins by assessing the types of strategic risk that can affect your organisation.
- Understanding organisational strategy: To measure the potential consequences of strategic risk, you must first thoroughly understand the organisation’s strategy and objectives. In this way, you can then prioritise potential risks.
- Gather data of strategic risk: By interviewing executives and stakeholders, you can gather data on how people in the organisation view strategic risk. Data gathering may be conducted with both internal and external personnel who would be affected by the risk. The use of automation tools and risk management software is highly effective in collecting data and helping to assess the risks that could affect your organisation. It also enables business more clarity across the business, map out processes, and set real-time alerts reducing bottlenecks, reducing data errors, removing critical man dependency and increasing compliance.
- Prepare strategic risk profile: With the information from step 1 and 2, you can create a strategic risk profile for the organisation. It can be displayed in a list or even a heat map to outline what the top strategic risks are and how severely they rank in terms of potential detrimental impacts.
- Validate the profile: Before creating a strategic risk management action plan, be sure that key executives and directors agree on the risk profile.
- Develop an action plan: Developing an action plan is the primary goal of this whole process. In this step, you will outline how the organisation plans to face, mitigate, ignore or overcome strategic risks. It also involves defining methods by which strategic risks will be managed.
- Communicate and implement the plan: Once you have the strategic risk management plan, then you must share the message across the organisation. Defining your organisation’s risk culture is what allows employees and team members to act in accordance.
Integrating Strategic Risk Management
Since strategic risk is tied to an organisation’s strategies, strategic risk management must become incorporated with the organisation’s core processes.
To embed strategic risk management into the organisation’s inner workings, you can follow these six steps to integrate risk management with strategic planning:
1. Develop the strategy: Define your mission and vision, as well as the ways by which you will assess risks.
2. Communication: Be sure to communicate with stakeholders and the internal team as to why strategic risk management is aligned with everyone’s interests. You can agree to regular updates and discussions about progress or gaps in the process.
3. Align the organisation: Review existing processes and procedures to ensure that risk management is incorporated and addressed. If anything is out-of-date or lacking information, provide updates.
4. Plan operations: Train everyone to understand how they can implement best practices to avoid or monitor strategic risks.
5. Monitor: Be sure to keep an eye on how processes are running and how business goals are being affected. Analysing data and monitoring KPIs is crucial to ensure that you are “doing the right things” to achieve business goals. One of the easiest ways to monitor KPIs in real-time is to utilise an automation tool because you can continuously track KPIs via dashboards.
6. Test and adapt: After implementation, keep an eye on the system. Perform quality-reviews and don’t be afraid to make changes if needed.

5 Tips for Success: Measuring and Managing Risk
Here are the top 5 tips for measuring and managing strategic risk in any business.
1. Define business goals: Many companies fail to integrate risk or acknowledge risk when defining their business goals. In this stage, it is crucial to outline the types of risks that can threaten your organisation. You can accomplish this in a simple exercise like using SWOT analysis.
2. Establish KPIs: Key performance indicators (KPIs) are a way to measure your success and downfalls. Decide what you want to measure and monitor, like sales per customer, for example. You can leverage automation solutions to provide you with dashboards of live updates of these numbers so you can assess if your processes are working in your favour.
3. Identify Risks: Risks are unknown situations that can affect variability in your KPIs and performance. Create a list of such risks so that when your business is concerned, you can quickly understand what’s happening to resolve the situation.
4. Define risk tolerance levels: KRIs, or key risk indicators, anticipate risks in advance. If you set your risk tolerance levels, then you can count on an automated tool to alert you in advance or manage the situation automatically once the threshold is met.
5. Provide reporting and monitoring: To stay abreast of how your organisation is doing, you want to continue to monitor risks and manage situations as they arise.
How Automation Helps
You can leverage automation tools to help assess and monitor strategic risks. Once you’ve devised your strategic risk management policy, you can note thresholds and criteria into your automation tool. This way, you can rely on the tool to provide you with updates if something is going wrong. By using quantitative analysis, you can be sure to track your business’ performance and see that it is headed in the right direction to accomplish business goals.
You can also use analysis to test business decisions and their potential effects before implementing them. Data analytics can provide you with the necessary information to make the right decisions, or in other words, do the right things for your business. Automation tools give a variety of benefits, including:
- Removal of low-level manual tasks
- Frees time for your team to focus on their high-value tasks
- Reduces human errors to improve the accuracy of information and reporting
- Improves compliance by providing audit trails and reports
- Provides real-time reporting for real-time insights and analysis
- Maps out processes to improve standardisation and consistency
- Offers trend analysis and data analytics for better decision-making and more precise insights
- Can be set up to provide real-time alerts and notifications
Types of Risk
We’ve already briefly touched on the differences between organisational and strategic risks. There are different types of risks that a business faces. Here’s a look at some types of risk so you can better understand how to approach them.
Category 1: Preventable risks
Preventable risks occur internally. They are breakdowns in processes that can otherwise be controlled. For the most part, avoidable risks are operational risks. One way to minimise operational risks is to set up business processes and use automation tools to run them. In this way alone, you can minimise various risks from a human error to eliminating bottlenecks.
Category 2: Strategy risks
To receive returns from business practices, organisations assume strategic risks. Strategic risks are not always undesirable; they are inherent as a part of running a business. Strategy risks cannot be controlled on a rules-basis method, like operational risks can. Instead, you need to devise the risk management system to reduce risk or manage them when they happen.
Category 3: External risks
Factors beyond a business’ control cause external risks. This includes natural and political disasters. External threats cannot be avoided, but they can be mitigated by creating action plans for if and when they occur.
A CFO’s Approach to Strategic Risk Management
A CFO plays an integral role in approaching strategic risk management. Strategic risks affect business plans, so it’s up to a CFO to help identity, assess and mitigate such risks. If you’re a CFO, you can get involved by:
- Stress testing: How will risks affect the business plan? Once you have this answer, you can incorporate stress testing as a part of the financial planning phase.
- Risk analytics: Before moving forward on any plan or investment, a CFO should conduct due diligence and use data automation software to carry out risk analytics to assess potential financial outcomes of any decision. With risk analytics, you can use historical data to help predict the future through predictive analytics.
- Risk preferences: To usher in rewards, the risk is necessary. However, it’s up to executive leadership to decide how much risk is worth taking on to move forward.
The Bottom Line
With strategic risks, businesses face both their most significant upsides and downfalls. To position your organisation to manage strategic risks adequately, it’s necessary to implement strategic risk management. An automation tool can help you better manage risks of every kind, including strategic risks.
Coming Up
2. What are Strategic Risk Examples
3. How to Overcome Different Types of Strategic Risk?
4. Strategic Risk vs Operational Risk
5. What is Strategic Risk Management?
6. Strategic Risk Assessment Process
7. Integrating Strategic Risk Management
8. 5 Tips for Success: Measuring and Managing Risk
11. A CFO’s Approach to Strategic Risk Management
What is Strategic Risk?
In its most simplistic of definitions, strategic risk is the risk associated with failed business decisions. It refers to decisions or events that can get in the way of an organisation reaching its goals.
Strategic risk represents one type of risk that businesses face, along with risks like operational, financial, and regulatory, to name a few. In many instances, strategic risks and the other kinds of risk will impact one another as they are interconnected.
Strategic risk can take place due to competition, market events, changing regulations, compliance, and more. We’ll soon touch on what this could look like in your business.
These types of risks affect overall business strategy, but sometimes they are necessary to reap the rewards. For example, a bank takes on strategic risk by offering credit, but it’s an inherent risk that is directly related to its business goals. Since strategic risk is all centered around “doing the right things,” it may be harder to identify than operational risks, which come down to “doing things right.”
Strategic risks occur when businesses fail to meet the market’s needs. To achieve business goals, companies face dangers and downfalls. Every internal choice comes with the potential of making the wrong choice. To complicate things further, strategic risk isn’t only based on subjective decisions. It can also be caused by externally because of market demand and the environment in which products get released.
What are Strategic Risk Examples
By breaking down strategic risk examples, we can better understand how to overcome them. Here’s a look at what they can be categorised as:
- Competitive risk: This refers to the risk that your competition will gain more market share than you and you will fall behind them in innovation.
- Regulatory risk: The degree to which you must adhere to regulations varies by industry. In highly regulated industries like finance or transportation, this type of strategic risk will clearly be more of a concern. This is because new regulations can affect your business processes, call upon the need for new roles to be created, demand new technologies, and shift your business leaders’ time and focus to having to deal with the regulations.
- Political risk: Changes in the political landscape can affect business’ operations, trade agreements, and more. Additionally, the politics affect security and the supply chain, so politics can pose a risk to businesses.
- Governance risk: Any risk associated with lack of governance or compliance. Again, the degree to which this risk affects your business will depend on your business line. When it comes to data and finances, governance risk is higher (which calls upon the need for more internal controls).
- Economic risk: The overall macroeconomic conditions affect how your business takes place and the success of your business strategy.
- Operational risk: This refers to the day-to-day ways that you execute in business and the risk that processes are not up-to-date. With outdated processes, you may be costing the business more or less productive than you’d otherwise be with process improvement.
- Change risk: Implementing changes within your organisation can create risk in itself if there’s resistance or struggles to adopt the change. Keep in mind that you can practice change management to overcome such risk.
How to Overcome Different Types of Strategic Risk?
The connection between the types of strategic risk can serve to your advantage. It requires a holistic and high-level view of your business, goals, and strategy to decide how to mitigate the strategic risks you may face.
With that said, here are suggestions for overcoming such risks:
- Understand your competition and conduct market research
- Utilise data to your advantage for business intelligence and forecasting
- Remain aware of regulatory changes and adopt technologies and processes that are agile
- Select suppliers and vendors in politically stable countries
- Continuously monitor your business and its practices to protect against financial risks
- Leverage change management such that change is welcomed and understood by everyone involved
No matter what type of strategic risks your business faces, financial automation software can serve multiple purposes. You can rely on having data in a centralised and secure location. You will be able to measure the success of your processes and optimise efficiency. You can conduct data analysis to make use of historical data to predict future events and be prepared.
Strategic Risk vs Operational Risk
To better understand strategic risk, it helps to define what operational risk is to see the differences.
Operational Risk: Operational risks comes from how a business does something, or in other words, their operations. Risks can arise from a breakdown in processes, people or systems. These risks stem from how a business performs day-to-day activities.
Now that we better understand what strategic risk is and isn’t, how do business leaders plan around strategic risk? They implement strategic risk management.
What is Strategic Risk Management?
Once you recognise and acknowledge that strategic risk is inherent in the business, it pays to manage it.
Strategic risk management is the process of identifying risks, analysing their potential effects and taking necessary action to mitigate them. These internal and external risks pose a threat to the business’ strategy and objectives. For example, if a finance company is going to sign a big new client, there is an inherent risk that the company won’t be able to scale quickly to provide the full service with the client needs and what if the client leaves after a short time. However, the finance company is aware of this risk and can plan by hiring part-time staff or keep existing staff and free up their time by driving more efficiencies such as through automation tools to mitigate such risk.
As a focal point under enterprise risk management (ERM), strategic risk management focuses on the types of risks that will affect stakeholder value. As such, executive-level leadership must allocate their time to help manage and face this risk.
Some examples of strategic risk include:
- Technological changes
- Senior management turnover
- Merger integration
- Stakeholder pressure
- Competitive pressure
- Consumer demand shifts
- Consumer preferences changes
- Regulatory changes
It’s critical to assess the impact of strategic risks to prioritise the strategy to manage them. The main two crucial metrics by which to evaluate strategic risks are:
- Economic Capital: This is the amount of equity needed to cover unexpected losses. It’s derived from the company’s target debt rating.
- Risk-Adjusted Return On Capital (RAROC): RAROC helps to understand the return on investment with the risk involved. It determines the return level relative to the risk taken. The calculation is: revenue - expenses - expected loss + income from capital / capital
Strategic Risk Assessment Process
Putting strategic risk management in action involves several steps. It begins by assessing the types of strategic risk that can affect your organisation.
- Understanding organisational strategy: To measure the potential consequences of strategic risk, you must first thoroughly understand the organisation’s strategy and objectives. In this way, you can then prioritise potential risks.
- Gather data of strategic risk: By interviewing executives and stakeholders, you can gather data on how people in the organisation view strategic risk. Data gathering may be conducted with both internal and external personnel who would be affected by the risk. The use of automation tools and risk management software is highly effective in collecting data and helping to assess the risks that could affect your organisation. It also enables business more clarity across the business, map out processes, and set real-time alerts reducing bottlenecks, reducing data errors, removing critical man dependency and increasing compliance.
- Prepare strategic risk profile: With the information from step 1 and 2, you can create a strategic risk profile for the organisation. It can be displayed in a list or even a heat map to outline what the top strategic risks are and how severely they rank in terms of potential detrimental impacts.
- Validate the profile: Before creating a strategic risk management action plan, be sure that key executives and directors agree on the risk profile.
- Develop an action plan: Developing an action plan is the primary goal of this whole process. In this step, you will outline how the organisation plans to face, mitigate, ignore or overcome strategic risks. It also involves defining methods by which strategic risks will be managed.
- Communicate and implement the plan: Once you have the strategic risk management plan, then you must share the message across the organisation. Defining your organisation’s risk culture is what allows employees and team members to act in accordance.
Integrating Strategic Risk Management
Since strategic risk is tied to an organisation’s strategies, strategic risk management must become incorporated with the organisation’s core processes.
To embed strategic risk management into the organisation’s inner workings, you can follow these six steps to integrate risk management with strategic planning:
1. Develop the strategy: Define your mission and vision, as well as the ways by which you will assess risks.
2. Communication: Be sure to communicate with stakeholders and the internal team as to why strategic risk management is aligned with everyone’s interests. You can agree to regular updates and discussions about progress or gaps in the process.
3. Align the organisation: Review existing processes and procedures to ensure that risk management is incorporated and addressed. If anything is out-of-date or lacking information, provide updates.
4. Plan operations: Train everyone to understand how they can implement best practices to avoid or monitor strategic risks.
5. Monitor: Be sure to keep an eye on how processes are running and how business goals are being affected. Analysing data and monitoring KPIs is crucial to ensure that you are “doing the right things” to achieve business goals. One of the easiest ways to monitor KPIs in real-time is to utilise an automation tool because you can continuously track KPIs via dashboards.
6. Test and adapt: After implementation, keep an eye on the system. Perform quality-reviews and don’t be afraid to make changes if needed.

5 Tips for Success: Measuring and Managing Risk
Here are the top 5 tips for measuring and managing strategic risk in any business.
1. Define business goals: Many companies fail to integrate risk or acknowledge risk when defining their business goals. In this stage, it is crucial to outline the types of risks that can threaten your organisation. You can accomplish this in a simple exercise like using SWOT analysis.
2. Establish KPIs: Key performance indicators (KPIs) are a way to measure your success and downfalls. Decide what you want to measure and monitor, like sales per customer, for example. You can leverage automation solutions to provide you with dashboards of live updates of these numbers so you can assess if your processes are working in your favour.
3. Identify Risks: Risks are unknown situations that can affect variability in your KPIs and performance. Create a list of such risks so that when your business is concerned, you can quickly understand what’s happening to resolve the situation.
4. Define risk tolerance levels: KRIs, or key risk indicators, anticipate risks in advance. If you set your risk tolerance levels, then you can count on an automated tool to alert you in advance or manage the situation automatically once the threshold is met.
5. Provide reporting and monitoring: To stay abreast of how your organisation is doing, you want to continue to monitor risks and manage situations as they arise.
How Automation Helps
You can leverage automation tools to help assess and monitor strategic risks. Once you’ve devised your strategic risk management policy, you can note thresholds and criteria into your automation tool. This way, you can rely on the tool to provide you with updates if something is going wrong. By using quantitative analysis, you can be sure to track your business’ performance and see that it is headed in the right direction to accomplish business goals.
You can also use analysis to test business decisions and their potential effects before implementing them. Data analytics can provide you with the necessary information to make the right decisions, or in other words, do the right things for your business. Automation tools give a variety of benefits, including:
- Removal of low-level manual tasks
- Frees time for your team to focus on their high-value tasks
- Reduces human errors to improve the accuracy of information and reporting
- Improves compliance by providing audit trails and reports
- Provides real-time reporting for real-time insights and analysis
- Maps out processes to improve standardisation and consistency
- Offers trend analysis and data analytics for better decision-making and more precise insights
- Can be set up to provide real-time alerts and notifications
Types of Risk
We’ve already briefly touched on the differences between organisational and strategic risks. There are different types of risks that a business faces. Here’s a look at some types of risk so you can better understand how to approach them.
Category 1: Preventable risks
Preventable risks occur internally. They are breakdowns in processes that can otherwise be controlled. For the most part, avoidable risks are operational risks. One way to minimise operational risks is to set up business processes and use automation tools to run them. In this way alone, you can minimise various risks from a human error to eliminating bottlenecks.
Category 2: Strategy risks
To receive returns from business practices, organisations assume strategic risks. Strategic risks are not always undesirable; they are inherent as a part of running a business. Strategy risks cannot be controlled on a rules-basis method, like operational risks can. Instead, you need to devise the risk management system to reduce risk or manage them when they happen.
Category 3: External risks
Factors beyond a business’ control cause external risks. This includes natural and political disasters. External threats cannot be avoided, but they can be mitigated by creating action plans for if and when they occur.
A CFO’s Approach to Strategic Risk Management
A CFO plays an integral role in approaching strategic risk management. Strategic risks affect business plans, so it’s up to a CFO to help identity, assess and mitigate such risks. If you’re a CFO, you can get involved by:
- Stress testing: How will risks affect the business plan? Once you have this answer, you can incorporate stress testing as a part of the financial planning phase.
- Risk analytics: Before moving forward on any plan or investment, a CFO should conduct due diligence and use data automation software to carry out risk analytics to assess potential financial outcomes of any decision. With risk analytics, you can use historical data to help predict the future through predictive analytics.
- Risk preferences: To usher in rewards, the risk is necessary. However, it’s up to executive leadership to decide how much risk is worth taking on to move forward.
The Bottom Line
With strategic risks, businesses face both their most significant upsides and downfalls. To position your organisation to manage strategic risks adequately, it’s necessary to implement strategic risk management. An automation tool can help you better manage risks of every kind, including strategic risks.
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

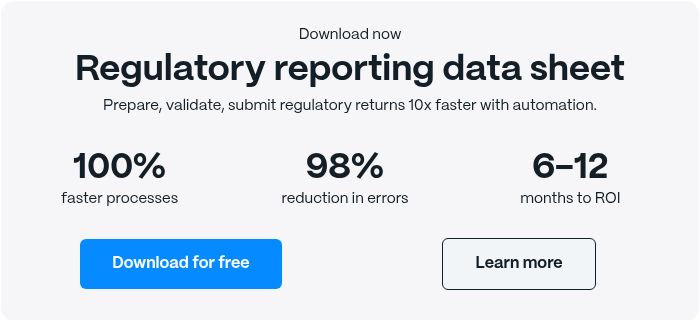
Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)